A newly disclosed vulnerability in ModSecurity, one of the most widely adopted Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), has raised alarms in the cybersecurity community. This flaw enables attackers to launch Denial of Service (DoS) attacks by sending empty XML tags in crafted HTTP requests, effectively rendering web servers unresponsive.
Why ModSecurity Is Critical
ModSecurity is an open-source WAF deployed globally to protect web applications from common attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and more. It inspects and filters HTTP requests against predefined security rules, serving as a crucial shield for millions of websites.
However, its ubiquity also makes it an attractive target. Any weakness can have far-reaching implications for businesses and users who rely on it for protection and uptime.
Understanding the Flaw
Researchers discovered that ModSecurity does not properly handle empty XML elements within HTTP request bodies. Specifically, when processing XML payloads that contain nested or repetitive empty tags, the WAF enters a resource-intensive state.
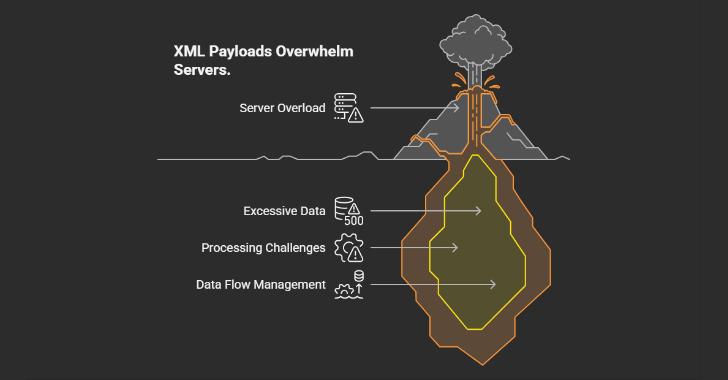
This leads to:
- Excessive CPU and memory consumption.
- Server performance degradation.
- Potential crashes and unavailability of the protected web service.
An attacker can exploit this by automating requests with malicious XML payloads, creating a sustained DoS condition without needing high bandwidth or advanced capabilities.
The Risk in Practice
Unlike vulnerabilities that allow data theft or remote code execution, this flaw primarily impacts availability. However, downtime can translate into financial loss, reputational damage, and customer dissatisfaction, making it a serious concern.
Attackers could also leverage the disruption as a smokescreen to mask additional malicious activity or to exhaust incident response resources.
Recommended Mitigations
Security and IT teams should act promptly to reduce exposure:
- Apply updates: Check the official ModSecurity repository for patches addressing this issue and upgrade immediately.
- Harden configurations: If your application does not require XML processing, configure the WAF to block or filter XML content.
- Enforce request limits: Implement request body size and rate limits to mitigate resource abuse.
- Monitor traffic: Analyze logs for unusual patterns, particularly repetitive or large XML payloads with empty elements.
Proactive monitoring and layered defenses can help mitigate both known and emerging attack vectors.
Key Lessons Learned
This vulnerability highlights critical truths about cybersecurity:
- Even trusted security tools can harbor weaknesses.
- Regular updates, testing, and hardening are non-negotiable.
- Availability is as important as confidentiality and integrity in protecting business operations.
Organizations should continually review their defenses, not only against external threats but also to ensure their security stack itself cannot be turned against them.